Description
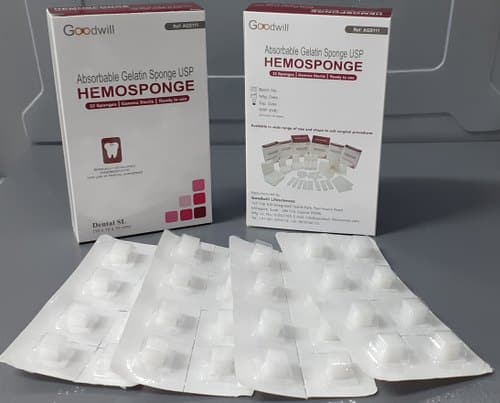
A hemospong, short for hemostatic sponge, is a specialized medical device designed to control bleeding by absorbing blood and promoting clot formation. Hemosponges are essential in various surgical, dental, and emergency settings where quick and efficient bleeding control is crucial. They are often used during operations, wound care, and trauma situations. This guide will provide an overview of hemosponges, their types, uses, and benefits, as well as important considerations for their application.
What is a Hemospong?
A hemospong is a sterile, bio-compatible sponge designed to stop bleeding (hemostasis) by rapidly absorbing blood. The sponge promotes clot formation by providing a surface for platelets to aggregate and by physically blocking the flow of blood. Hemosponges are made from materials like gelatin, cellulose, or collagen, and are often impregnated with clotting agents such as thrombin to enhance their effectiveness.
How Hemosponges Work
Hemosponges function by creating a physical barrier over the bleeding site, absorbing blood, and facilitating the body’s natural clotting process. The porous structure of the sponge allows it to absorb large amounts of blood while providing a surface for platelets to gather and form clots. In some cases, hemosponges are treated with clotting factors, which accelerate the hemostasis process.
Types of Hemosponges
1. Gelatin-Based Hemosponges
Gelatin-based hemosponges are commonly used in surgical settings. These sponges absorb blood and expand, applying pressure to the bleeding area to stop the flow of blood. They are resorbable and are gradually broken down by the body over time.
Use Cases:
Surgical procedures (orthopedic, cardiovascular)
Trauma management
Dental extractions
Advantages:
Resorbable, so no need for removal
Easy to use
Reduces blood loss effectively
2. Collagen-Based Hemosponges
Collagen hemosponges are derived from animal tissues and are excellent at accelerating clot formation. Collagen is a natural component of connective tissue, so it works in harmony with the body’s clotting mechanisms.




Reviews
There are no reviews yet.